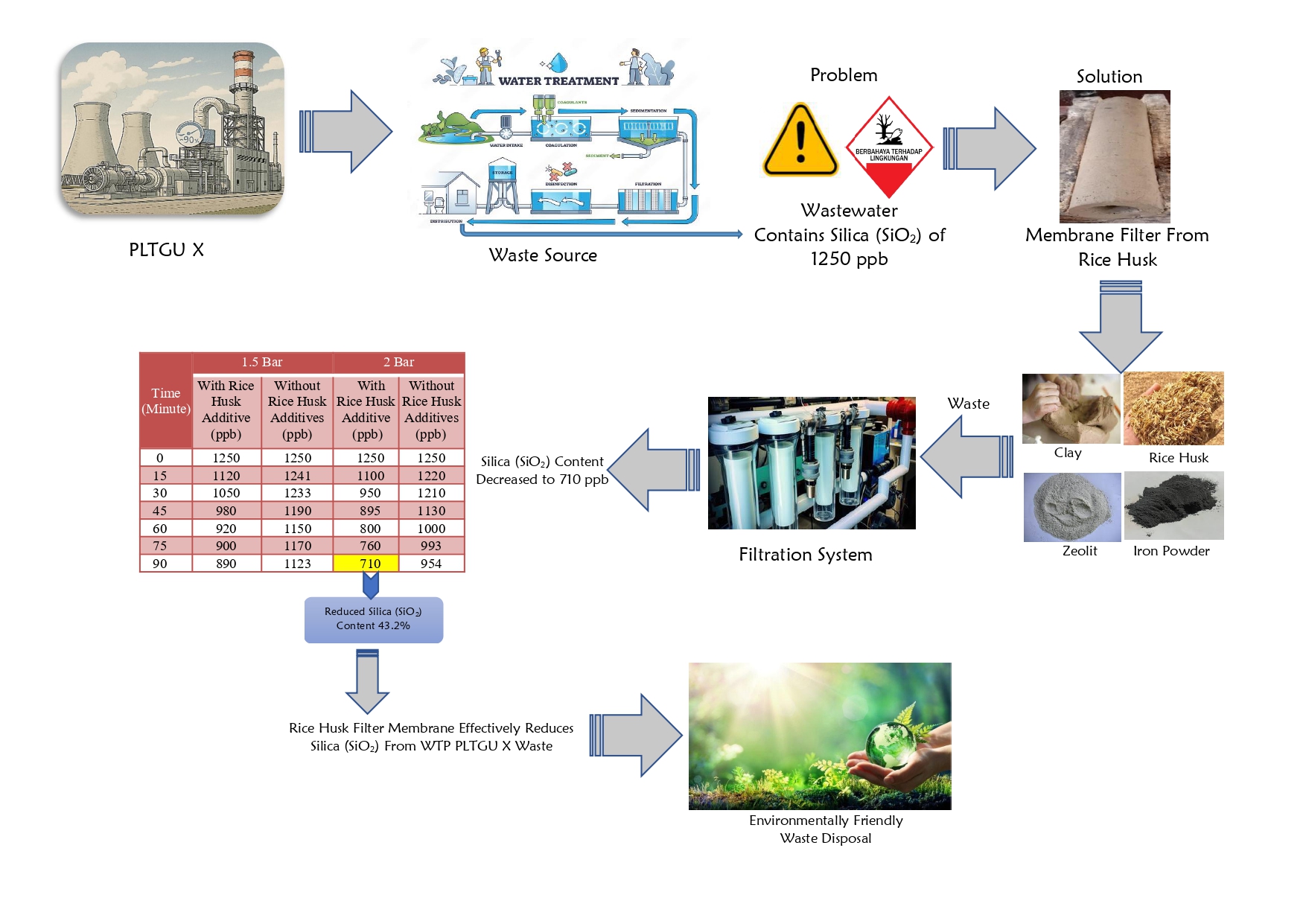
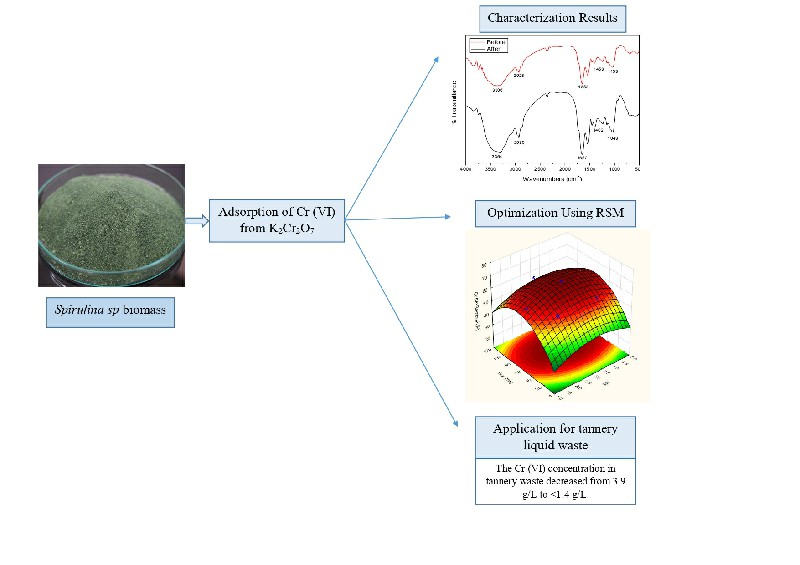
Optimization of Chromium (VI) Adsorption using Microalgae Biomass (Spirulina sp.) and its Application in Leather Tannery Waste
Downloads
This study was conducted to examine the adsorption of Cr (VI) metal using Spirulina sp (inactive) biomass and its application in leather tannery wastewater. The treatment was carried out to determine the influence of independent variables on Cr (VI) adsorption with variations in pH, contact time, and metal solution concentration. The values of the solution pH, adsorption time, and concentration of the best metal solution were used to determine the center points of the optimization variables through Response Surface Methodology (RSM). The results showed that based on the FTIR test, macromolecules present in Spirulina sp biomass included amino, carboxylate, and hydroxy groups. The combination of factor variables that produced the optimum response was at pH 3.165, contact time of 66.58 minutes, and Cr (VI) metal ion solution concentration of 22.9 mg/L, resulting in a Cr (VI) adsorption efficiency of 69.66%. The adsorption pattern was included in the Freundlich adsorption isotherm, and the application of Spirulina sp biomass adsorbent to tannery waste reduced the concentration of Cr (VI) from 3.9 g/L to an undetectable level at <1.4 g/L.
Downloads
[1] Kuncoro, Y. M., & Soedjono, E. S. (2022). Studi Pustaka: Teknologi Pengolahan Air Limbah pada Industri Penyamakan Kulit. Jurnal Teknik ITS, 11(3). DOI: 10.12962/j23373539.v11i3.99654
[2] Astuti, D., Sukmawati, N., Asyfiradayati, R., & Darnoto, S. (2022). Kajian Literatur Tentang Reduksi Kromium dalam Air Limbah Penyamakan Kulit dengan Fitoremediasi. Syntax Literate; Jurnal Ilmiah Indonesia, 7(1), 146. DOI: 10.36418/syntax-literate.v7i1.5723
[3] Endah, T., Buhani, & Suharso. (2015). Immobilization of cocodust biomass with silica gel as adsorbent for Cd ( II ) and Pb ( II ) ions in solution. In Proceeding of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (pp. 56-60).
[4] Pradhan, D., Sukla, L. B., Mishra, B. B., & Devi, N. (2019). Biosorption for removal of hexavalent chromium using microalgae Scenedesmus sp. Journal of Cleaner Production, 209, 617-629. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.288
[5] Rezaei, H. (2016). Biosorption of chromium by using Spirulina sp. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 9(6), 846-853. DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.11.008
Copyright (c) 2023 CHEESA: Chemical Engineering Research Articles

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
With the receipt of the article by CHEESA Editorial Board and the decision to be published, the copyright regarding the article will be transferred to CHEESA Journal.
CHEESA has the right to multiply and distribute the article and every author is not allowed to publish the same article that was published in this journal.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Under the following terms:
Attribution ” You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial ” You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
ShareAlike ” If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.