Reducing Silica Levels in WTP PLTGU X Wastewater using Rice Husk Filter Membranes
Penurunan Kadar Silika pada Air Limbah WTP PLTGU X Menggunakan Membran Filter Sekam Padi
Downloads
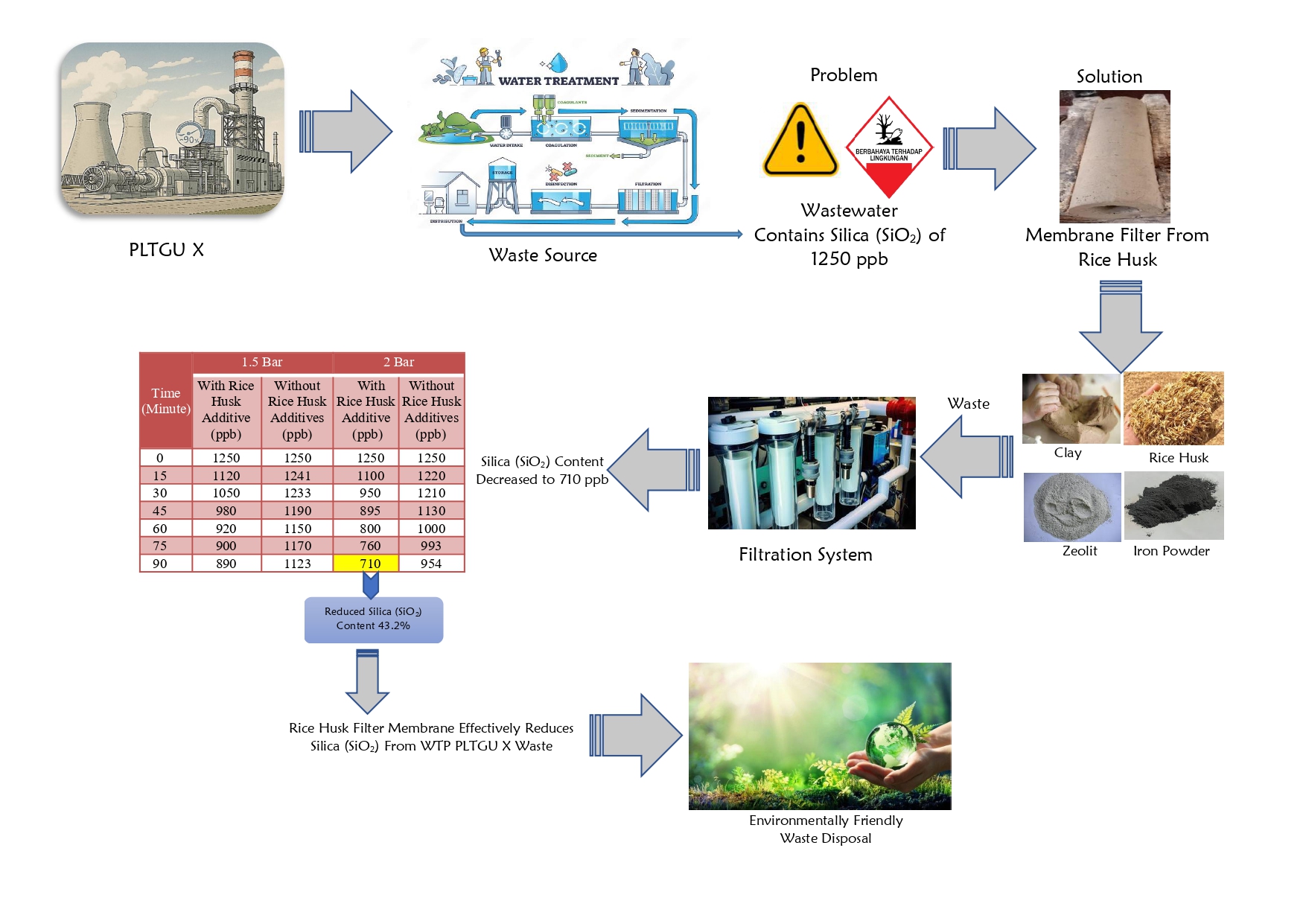
During the water demineralization process, silica content is increased due to the failure of the chemical reagent. This shows the need to perform a blowdown action to reduce silica content in the water. Therefore, this research aimed to determine the effectiveness of silica reduction in the Water Treatment Plant (WTP) of PLTGU X by observing the permeate flux values relative to time and operating pressure variables, using ceramic membrane made from rice husk. To achieve the objective, ceramic membrane was made from rice husk additives, with a pore diameter of 365 nm and a surface area of 25 cm². The results showed that the composition ratio of clay, rice husk, and iron powder was 82.5%, 15%, and 2.5%, respectively. Furthermore, ceramic membrane with rice husk additives successfully reduced silica content from 1250 ppb to 890 ppb at a pressure of 1.5 bar and 90 minutes of operation and from 1250 ppb to 710 ppb at 2 bar and 90 minutes of operation. This suggested that wastewater could be processed again in the demineralization plant to produce demineralized water. The best membrane performance in the filtration process was achieved at 90 minutes with a pressure of 2 bar, which successfully reduced silica content by 43.2%, with a permeate flux of 3.44 L/m².
Downloads
Arazaq. T., Sefentry. A., & Husnah. (2021). Perbandingan Pengolahan Air Limbah Karet Antara Dua Membran Keramik. Jurnal Redoks. 6 (1), (72-79) https://doi.org/10.31851/redoks.v6i1.5201.
Putri, A. F., & Setorini, I. A. (2023). Pembuatan Membran Keramik Berbahan Dasar Tanah Liat, Serbuk Daun Kelor, dan Arang Aktif untuk Menurunkan Kekeruhan dan Meningkatkan Nilai pH Sampel Air Sungai Musi. Journal of Innovation Research and Knowledge, 2(10), 4285–4294. https://doi.org/10.53625/jirk.v2i10.5471.
Mayasari, R., Djana, M., Rosalia D.W., Anwar, H., & Haviz, M. (2024). Karakteristik Membran Keramik Berpori Berbahan Baku Bentonit Dan Zeolit Dengan Proses Ekstrusi. Jurnal Redoks, 9(1), (93–98). https://doi.org/10.31851/redoks.v9i1.15361.
Darmayanti, L, Putri, M., & Edward, H.S. (2022). Membran Keramik Berbahan Dasar Tanah Liat dan Fly Ash untuk Penyisihan Warna dan Zat Organik pada Air Gambut. Jurnal Rekayasa Sipil dan Lingkungan, 6 (1), (1-15). https://doi.org/10.19184/jrsl.v6i1.28173
Rahmat. A. Y., Syahbanu. I & Rudiyansyah. (2020). Membran Ultrafiltrasi Polisulfon/TiO2 (Psf/TiO2) Sebagai Filter Pada Pencemaran Air Oleh Bahan Bakar Solar. J. Kartika Kimia, 3(1), (7-12). https://doi.org/10.26874/jkk.v3i1.46.
Yuliwati. E., Martini. S.,& Melani. A.,(2021). Teknologi Membran Ultrafiltrasi Untuk Pengelolaan Air Limbah Pencucian Industri Tekstil Eco-Print. Publikasi Penelitian Terapan Dan Kebijakan. 4 (1). (35-42). https://doi.org/10.46774/pptk.v4i1.342
Bhernama. B.G., Nurhayati, Saputra. S.A., & Amalia.J., (2023). Characterization Of Cellulose Acetate Membrane From Nutmeg Shells. Jurnal Sains Natural. 13(3). (152–160).https://doi.org/10.31938/jsn.v13i3.465.
Fransiska. D., Yuliati. S., & Junaidi. R. (2023). Membran Selulosa Asetat Berbasis Nata De Coco Ditinjau dari Pengaruh Penambahan Zat Aditif Polyethylene Glycol Terhadap Permeabilitas (Fluks). Jurnal Serambi Engineering. 8(4), (7078 - 7085). https://doi.org/10.32672/jse.v8i4.6739.
Shahab, A., Faputri, A., & Putra, W. (2023) Perbandingan Hasil Analisa Pemurnian Air Sumur Bor Menggunakan Membran Selulosa Asetat Hasil Ekstraksi Eceng Gondok Dan Pelepah Pisang Dengan Penambahan ZnO Dan Kulit Bawang Putih. Jurnal Teknik Patra Akademika. 14(02). (92-100). https://doi.org/10.52506/jtpa.v14i02.217.
Bramanta, K., A., Prasetia, A., M,D, & Susilowati. (2023). Pemanfaatan Limbah Sabut dan Tempurung Kelapa Sawit sebagai Silica Gel. Jurnal Ilmiah Universitas Batanghari Jambi. 23(2). 2366–2372. http://dx.doi.org/10.33087/jiubj.v23i2.3328.
Laelasari, R. Y. U., (2022). Aplikasi Membran Filter Keramik Dengan Penambahan Karbon Aktif Sekam Padi Untuk Menurunkan Kadar Cod, Fosfat Dan Surfaktan Limbah Cair Laundry. Repositori Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Kalijaga Yogyakarta. http://digilib.uin-suka.ac.id/id/eprint/51993
Mahfuzin. A.N., Respati, S.M.B., & Dzulfikar, M. (2020). Analisis Filter Keramik Berpori Berbasis Zeolit Alam Dan Arang Sekam Padi Dalam Menurunkan Kandungan Partikel Air Sumur Galian. Jurnal Ilmiah Momentum. 16(1). (63-68). http:// doi.org/10.36499/jim.v16i1.3363
Elfiana, E., Ridwan., Sami, M., Intan, S.K., & Rahmahwati, C.A., (2020). Klasifikasi dan Permselektifitas Membran Keramik Tubular Berbasis Zeolit Dan Variasi Clay-Karbon Aktif Berdasarkan Fluks, Permeabilitas Membran dan Koefesien Rejeksi Ion Fe dan Ion Mn dalam Air Tanah. Proceeding Seminar Nasional Politeknik Negeri Lhokseumawe. 4(1). (106-111). https://e-jurnal.pnl.ac.id/semnaspnl/article/view/2672/0
Farhana, M., Budiyono, B., Yunita Dewanti, N. A., & Widayatno, W. B. (2020). Reduce CO On Car By Using Zeolite. Widyariset, 6(2), (107-115). https://10.14203/widyariset.6.2.2020.107-115.
Ifandi, A., Sefentry, A., Masriatini, R., & Lelawati, L. (2023). Perbandingan Hasil Membran Keramik Buatan Dan Membran Keramik Pabrikan Pada Pengolahan Air Limbah Industri Tahu. Jurnal Redoks, 7(2), 67–73. https://doi.org/10.31851/redoks.v7i2.5199.
Sylvani, M. M., Yuneta., Simbolon, W., dan Susanti, R. (2023). Berbagai Macam Jenis Membran Untuk Pemulihan Air Gambut. Jurnal Ilmiah Multidisiplin. 1(5), (598-609). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8280003
Diana, S., Fauzan, R., Munawar., Habibah, U., dan Nahar, N.(2021). Penyisihan Logam Berat Timbal Dalam Air Limbah Industri Menggunakan Membran
Keramik Berbasis Fly Ash, Clay Dan Arang Aktif Tempurung Kelapa Sawit. Proceeding Seminar Nasional Politeknik Negeri Lhokseumawe. 5(1). (181-184). Politeknik Negeri Lhokseumawe
Van de Voort, F. (1997). Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications. Chapter 4. In Instrumental Methods in Food Analysis. J.R.J. Paré and J.M.R Bélanger, Eds. Elsevier Science B.V. (Pp 93-139).
Copyright (c) 2024 CHEESA: Chemical Engineering Research Articles

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
With the receipt of the article by CHEESA Editorial Board and the decision to be published, the copyright regarding the article will be transferred to CHEESA Journal.
CHEESA has the right to multiply and distribute the article and every author is not allowed to publish the same article that was published in this journal.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Under the following terms:
Attribution ” You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial ” You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
ShareAlike ” If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.