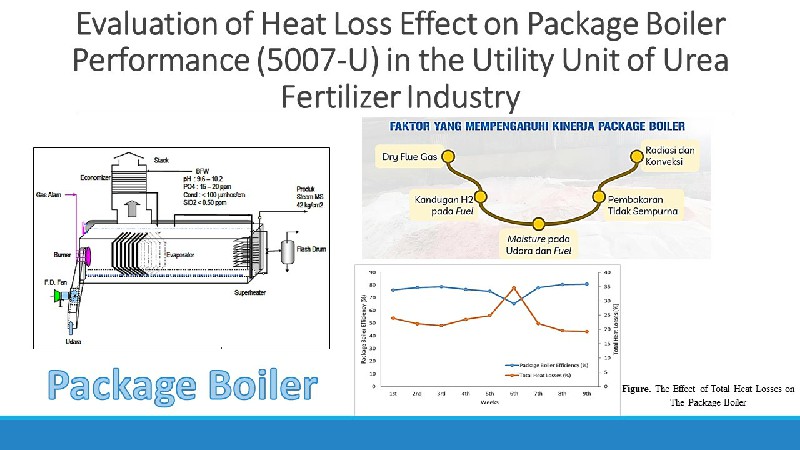
Produksi dan Optimasi Biosurfaktan dari Bakteri Halofilik Chromohalobacter japonicus BK-AB18
Downloads
Perkembangan teknologi bioproses telah mendorong pendekatan ke arah produk surfaktan biologi (biosurfaktan) yang ramah lingkungan. Penelitian ini difokuskan pada optimasi produksi biosurfaktan dengan menggunakan variasi sumber karbon dan nitrogen. Tahap awal penelitian ini dilakukan dengan menguji potensi bakteri Chromohalobacter japonicus BK-AB18 penghasil biosurfaktan dengan menggunakan metode uji hemolisis dimana hasil menunjukkan aktivitas hemolisis yang tinggi dengan ukuran zona bening 3 cm pada media agar darah. Selanjutnya dilakukan produksi pada medium optimal dengan menambahkan 2% variasi sumber karbon terdiri dari minyak zaitun, minyak jagung, minyak kelapa sawit, minyak kacang kedelai dan minyak bunga matahari serta 0,3 % variasi nitrogen terdiri dari urea, NaNO3, NH4Cl, NH2(SO)4 and KNO3. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan produksi biosurfaktan dari Chromohalobacter japonicus BK-AB18 meningkat secara signifikan dengan menggunakan minyak zaitun sebagai sumber karbon dan urea sebagai sumber nitrogen dengan hasil penyebaran minyak 4,8 cm serta aktivitas biosurfaktan dengan nilai tegangan permukaan sebesar 34 dyne/cm, dan hasil uji emulsifikasi sebesar 76%.
Downloads
Abouseoud, M., Maachi, R., Amrane, A., Boudergua, S., & Nabi, A. (2008). Evaluation of different carbon and nitrogen sources in production of biosurfactant by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Desalination, 223(1-3), 143-151.
Asfora, S. L., Moura de Luna, J., & de Campos-Takaki, G. M. (2006). Production and stability studies of the bioemulsifier obtained from a new strain of Candida glabrata UCP 1002. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 9(4), 0-0.
Astuti, D. I., Purwasena, I. A., Putri, R. E., Amaniyah, M., & Sugai, Y. (2019). Screening and characterization of biosurfactant produced by Pseudoxanthomonas sp. G3 and its applicability for enhanced oil recovery. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 1-11.
Asy'ari, M., Parwata, I. P., Aditiawati, P., Akhmaloka, A., & Hertadi, R. (2014). Isolation and identification of halostable lipase producing bacteria from the Bledug Kuwu mud crater located at Purwodadi-Grobogan, Central Java, Indonesia. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol, 8(5), 3387-3396.
Balan, S. S., Kumar, C. G., & Jayalakshmi, S. (2017). Aneurinifactin, a new lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by a marine Aneurinibacillus aneurinilyticus SBP-11 isolated from Gulf of Mannar: purification, characterization and its biological evaluation. Microbiological research, 194, 1-9.
Barragan, L. A. P, Figueroa, J. J. B., Duran, R. L. V., Gonzalez, C. N. A., Hennings, C. (2016). Biotransformation of Agricultural Waste and By-Products, 189-217, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803622-8.00007-0
Desai, J. D., & Banat, I. M. (1997). Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 61(1), 47-64.
Donio, M. B. S., Ronica, F. A., Viji, V. T., Velmurugan, S., Jenifer, J. S. C. A., Michaelbabu, M., ... & Citarasu, T. (2013). Halomonas sp. BS4, A biosurfactant producing halophilic bacterium isolated from solar salt works in India and their biomedical importance. SpringerPlus, 2(1), 149.
El-Sheshtawy, H. S., Aiad, I., Osman, M. E., Abo-ELnasr, A. A., & Kobisy, A. S. (2015). Production of biosurfactant from Bacillus licheniformis for microbial enhanced oil recovery and inhibition the growth of sulfate reducing bacteria. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 24(2), 155-162.
Henriet, O., Fourmentin, J., Delincé, B., & Mahillon, J. (2014). Exploring the diversity of extremely halophilic archaea in food-grade salts. International journal of food microbiology, 191, 36-44.
Ibrahim, H. M. (2018). Characterization of biosurfactants produced by novel strains of Ochrobactrum anthropi HM-1 and Citrobacter freundii HM-2 from used engine oil-contaminated soil. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 27(1), 21-29.
Janaki, S., Thenmozhi, S., & Muthumari, R. (2015). A study on Hydrocarbon Degradation by Biosurfactant Producing Bacillus cereus in Oil Contaminated Soil Samples. Int. J. Life. Sci. Scienti. Res, 2(4).
Kosaric, N., Cairns, W. L., Gray, N. C. C. (1987). Biosurfactants and Biotechnology. USA: Newyork and Bassel, Maecell Dekker, INC.
Kumar, C. G., Sujitha, P., Mamidyala, S. K., Usharani, P., Das, B., & Reddy, C. R. (2014). Ochrosin, a new biosurfactant produced by halophilic Ochrobactrum sp. strain BS-206 (MTCC 5720): purification, characterization and its biological evaluation. Process Biochemistry, 49(10), 1708-1717.
Makkar, R. S., & Cameotra, S. S. (1997). Biosurfactant production by a thermophilic Bacillus subtilis strain. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18(1), 37-42.
Morikawa, M., Hirata, Y., & Imanaka, T. (2000). A study on the structure-function relationship of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1488(3), 211-218.
Mulligan, C. N. (2005). Environmental applications for biosurfactants Environmental pollution, 133(2), 183-198.
Rahayu, S. (2015). Pengaruh sumber karbon dan nitrogen pada produksi biosurfaktan oleh bakteri Pseudomonas aerginosa BIOPA 2411 (Doctoral dissertation, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember).
Sarafin, Y., Donio, M. B. S., Velmurugan, S., Michaelbabu, M., & Citarasu, T. (2014). Kocuria marina BS-15 a biosurfactant producing halophilic bacteria isolated from solar salt works in India. Saudi journal of biological sciences, 21(6), 511-519.
Sharma, R., & Gupta, A. (2014). Differentiation of oral Streptococcal species by haemolysis in blood agar medium in vitro. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, 4, 143-144.
Suganthi, C., Mageswari, A., Karthikeyan, S., Anbalagan, M., Sivakumar, A., & Gothandam, K. M. (2013). Screening and optimization of protease production from a halotolerant Bacillus licheniformis isolated from saltern sediments. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 11(1), 47-52.
Ventosa, A., Nieto, J. J., & Oren, A. (1998). Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 62(2), 504-544
Copyright (c) 2019 CHEESA: Chemical Engineering Research Articles

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
With the receipt of the article by CHEESA Editorial Board and the decision to be published, the copyright regarding the article will be transferred to CHEESA Journal.
CHEESA has the right to multiply and distribute the article and every author is not allowed to publish the same article that was published in this journal.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Under the following terms:
Attribution ” You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial ” You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
ShareAlike ” If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.