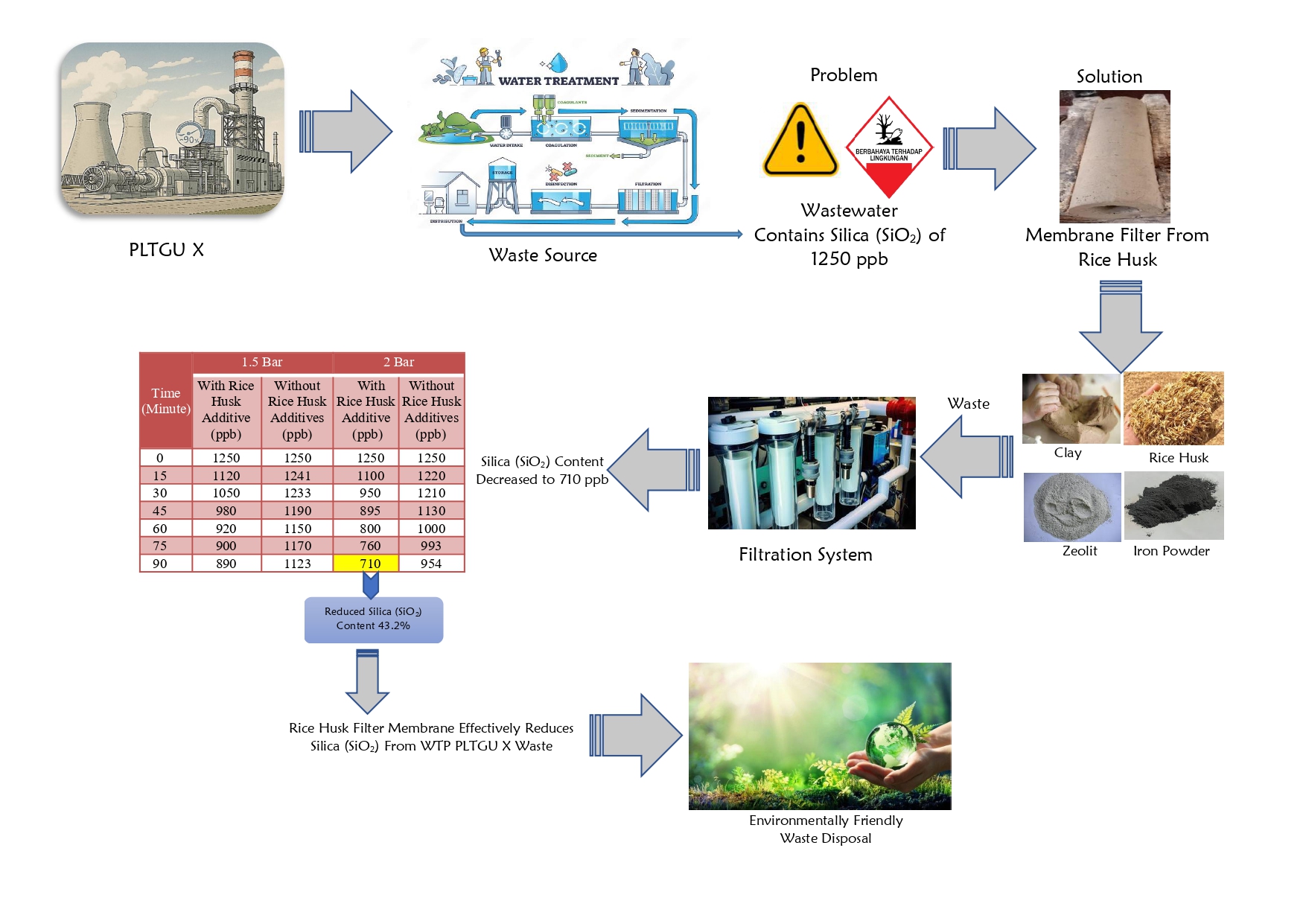
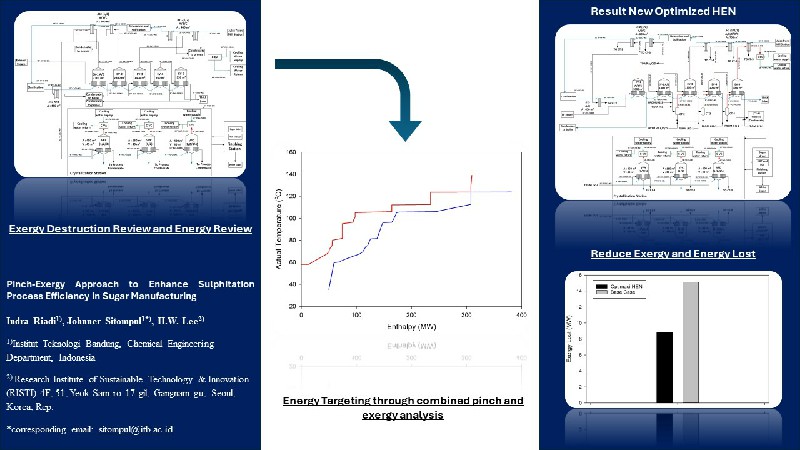
Pinch-Exergy Approach to Enhance Sulphitation Process Efficiency in Sugar Manufacturing
Downloads
This study aimed to enhance the thermal efficiency of the sulphitation process in the boiling house of sugar plants using a combined approach of pinch and exergy analyses. Pinch analysis is a reliable method for optimizing the design of energy recovery systems. However, the primary limitations arise from its exclusive focus on heat transfer processes. On the other hand, exergy balance provides valuable insight into the consumption of supplied exergy by individual process units, serving as a quantitative measure of inefficiency. The boiling house was evaluated and modified using pinch-exergy analysis with Sulphitation Process capacity production of 8000 TCD. The results showed a potential reduction in exergy destruction by approximately 10.25 MW. The optimization effort led to reductions of 18.18 and 14.70% in the use of hot and cold external utility, respectively.
Downloads
[1] Higa, M., Freitas, A. J., Bannwart, A. C., & Zemp, R. J. (2009). Thermal integration of multiple effect evaporator in a sugar plant. Applied Thermal Engineering, 29(2-3), 515-522. DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2008.03.009
[2] Sa, D. (2023). Economic Analysis of Separation Unit of Methanol to Propylene Production Based on Optimization of Refrigeration Cycles Using Pinch and Exergy Analysis. International Journal of Refrigeration, 146, 108-117. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2022.09.029
[3] Truls Gundersen, David Olsson Berstad, & Audun Aspelund. (2009). Extending pinch analysis and process integration into pressure and fluid phase considerations. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 18, 33-38. DOI: 10.3303/CET0918003
[4] Ramanath, T., Foo, D. C. Y., Tan, R. R., & Tan, J. (2023). Integrated enterprise input-output and carbon emission pinch analysis for carbon intensity reduction in edible oil refinery. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 193, 826-842. DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2023.03.045
[5] Kemp, I. C. (2007). Pinch analysis and process integration: a user guide on process integration for the efficient use of energy (2nd ed.). Amsterdam; Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann.
[6] Westphalen, D. L., & Wolf Maciel, M. R. (2000). Optimization of bleed streams in evaporation systems based on pinch analysis: new approach. Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, 8, 997-1002. Elsevier. DOI: 10.1016/S1570-7946(00)80168-6
[7] Singh, I., Riley, R., & Seillier, D. (1997). Using pinch technology to optimise evaporator and vapour bleed configuration at the malelane mill. Proc S Afr Sug Technol Ass, 71(207-216).
[8] Riadi, I., & Puji Utomo, D. (2022). The Effect of Operating Condition on Low Pressure Steam (LPS) in Sugar Factory by Pinch Analysis. UNISTEK, 9(1), 68-82. DOI: 10.33592/unistek.v9i1.1786
[9] Gaggioli, R. (1998). Available Energy and Exergy. Int.J. Applied Thermodynamics, 1(1-4), 1-8.
[10] Wan, T., Bai, B., & Zhou, W. (2023). Exergy destruction analysis of a power generation system utilizing the cold energy of LNG. Heliyon, e19393. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19393
[11] Kotas, T. (1995). The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis. Krieger Publishing Company.
[12] Ghorbani, B., Salehi, G. R., Ghaemmaleki, H., Amidpour, M., & Hamedi, M. H. (2012). Simulation and optimization of refrigeration cycle in NGL recovery plants with exergy-pinch analysis. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 7, 35-43. DOI: 10.1016/j.jngse.2012.03.003
[13] Pacheco-Cedeño, J. S., Rodríguez-Muñoz, J. L., Ramírez-Minguela, J. J., & Pérez-García, V. (2023). Comparison of an absorption-compression hybrid refrigeration system and the conventional absorption refrigeration system: Exergy analysis. International Journal of Refrigeration, S0140700723002177. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2023.08.003
[14] Cerci, Y. (2002). The minimum work requirement for distillation processes. Exergy, An International Journal, 2(1), 15-23. DOI: 10.1016/S1164-0235(01)00036-X
[15] Kumar Dhakar, M., Choudhary, P., & Singh, N. K. (2021). Performance improvement of a sugar mill through EXERGY analysis. Materials Today: Proceedings, 46, 11202-11207. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.427
[16] Peres, A. M., & Macedo, E. A. (1996). Thermodynamic properties of sugars in aqueous solutions: correlation and prediction using a modified UNIQUAC model. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 123, 71-95.
[17] Kylan, G., Annegret, S., & Maciet, S. (2019). Development and verification of an aspen plus® model of a sugarcane biorefinery. Proc S Afr Sug Technol Ass, 92, 254-273.
[18] Mafi, M., Naeynian, S. M. M., & Amidpour, M. (2009). Exergy analysis of multistage cascade low temperature refrigeration systems used in olefin plants. International Journal of Refrigeration, 32(2), 279-294. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2008.05.008
[19] Smith, J. M., Van Ness, H. C., Abbot, M. M., & Swihart, M. T. (2018). Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
[20] Pambudi, N., Laurensia, R., Wijayanto, D., Perdana, V., Saw, L., & Handogo, R. (2017). Exergy Analysis of Boiler Process Powered by Biogas Fuel in Ethanol Production Plant: A Preliminary Analysis. Energy Procedia, 142, 216-223. DOI: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.12.035
[21] Lambert, C., Laulan, B., Decloux, M., Romdhana, H., & Courtois, F. (2018). Simulation of a sugar beet factory using a chemical engineering software (ProSimPlus ® ) to perform Pinch and exergy analysis. Journal of Food Engineering, 225, 1-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.01.004
[22] Rein, P. (2007). Cane Sugar Engineering. Berlin: Verlag Dr. Albert Bartens KG.
[23] Zhang, K., Liu, Z., Huang, S., & Li, Y. (2015). Process integration analysis and improved options for an MEA CO2 capture system based on the pinch analysis. Applied Thermal Engineering, 85, 214-224. DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.03.073
Copyright (c) 2024 CHEESA: Chemical Engineering Research Articles

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
With the receipt of the article by CHEESA Editorial Board and the decision to be published, the copyright regarding the article will be transferred to CHEESA Journal.
CHEESA has the right to multiply and distribute the article and every author is not allowed to publish the same article that was published in this journal.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Under the following terms:
Attribution ” You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial ” You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
ShareAlike ” If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.