Pemodelan dan Simulasi Pencairan Gas Alam dengan Persamaan Keadaan Peng Robinson
Abstract
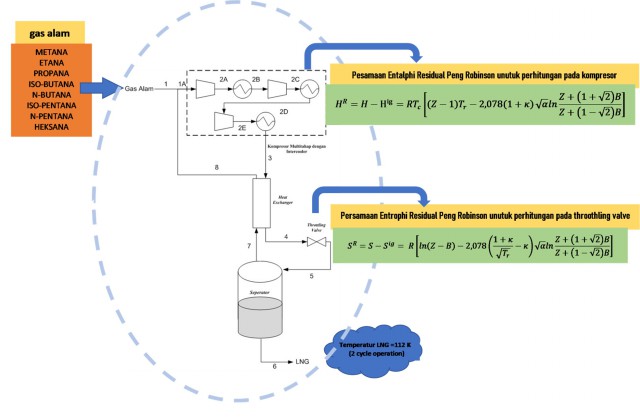
Gas alam merupakan energi yang ramah lingkungan dibandingkan batubara dan minyak bumi. Pencairan gas alam memudahkan pengangkutan pada jarak jauh. Tujuan pemodelan dan simulasi pencairan gas alam ini yaitu mengetahui pengaruh temperatur dan tekanan pada masukan kompresor. Simulasi dilakukan secara statis dan dinamis. Metode simulasi pencairan gas alam menggunakan perangkat Matlab dengan persamaan keadaan Peng Robinson dan aturan campuran (mixing rules). Pemodelan statisdilakukan pada temperatur masukan gas alam 298 K dan tekanan 20 atm. Hasil simulasi menunjukkan gas alam mengalami pencairan pada siklus kedua. Temperatur gas alam siklus pertama mencapai 182 K sedangkan kedua 112 K. Pemodelan dinamis memvariasikan temperatur masukan kompresor pada komposisi gas alam tetap dan variasi komposisi gas metana pada temperatur masukan kompresor tetap. Hasil menunjukkan semakin tinggi temperatur masukan kompresor, semakin tinggi temperatur keluaran kompresor akhir dan throttling valve. Pada variasi komposisi gas metana, semakin besar komposisi gas metana maka semakin rendah suhu keluaran kompresor.
Keywords
Full Text:
DOWNLOAD PDFReferences
Akinola, T. E., Oko, E., & Wang, M. (2019). Study of CO2 removal in natural gas process using mixture of ionic liquid and MEA through process simulation. Fuel, 236, 135–146, DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.08.152
Al-Breiki, M., & Bicer, Y. (2020). Technical assessment of liquefied natural gas, ammonia and methanol for overseas energy transport based on energy and exergy analyses. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45(60), 34927–34937, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.181
AlNouss, A., Ibrahim, M., & Al-Sobhi, S. A. (2018). Potential energy savings and greenhouse gases (GHGs) emissions reduction strategy for natural gas liquid (NGL) recovery: Process simulation and economic evaluation. Cleaner Production, 194, 525–539, DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.107
Fahmi, M., Fauzi, M., & Wibawa, G. (2013). Studi Awal Desain LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) Plant Dari Coal Bed Methane (CBM) Dengan Kapasitas Feed 40 MMSCFD. Jurnal Teknik ITS, 2(2), B224–B227, DOI: 10.12962/j23373539.v2i2.3556
Fatimura, M., & Fitriyanti, R. (2018). Penanganan Gas Asam ( Sour Gas ) Yang Terkandung Dalam Gas Alam Menjadi Sweetening Gas. Redoks, 3(2), 55, DOI: 10.31851/redoks.v3i2.2390
Ismail, M. (2014). Proses Pemurnian Gas Bumi sebagai Bahan baku Kilang Mini (Studi kasus Ladang Marginal Cikarang-Area Operasi Barat EP Pertamina). M.P.I, 8(1), 25–38, DOI: 10.29122/mipi.v8i1.3645
Khairunisa, A., Prabu, U.A., & Suwardi, F.R. (2015). Evaluasi Persiapan dan Pelaksanaan Proyek Komersialisasi Gas Lapangan X untuk memenuhi Syarat Volume dan Tekanan pada Kontrak Perjanjian Jual Beli Gas (PJBG) di Pertamina EP Asset 1 Field Jambi. Jurnal Ilmu Teknik, 3(2), 1-6, LINK
Kyle, B.G. (1999). Chemical and Process Thermodynamics. :Prentice- Hall.
Łaciak, M., Sztekler, K., Szurlej, A., & Włodek, T. (2019). Possibilities of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) use for power generation. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 214(1), DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/214/1/012138
Nakhjiri, A. T., Heydarinasab, A., Bakhtiari, O., & Mohammadi, T. (2020). Numerical simulation of CO2/H2S simultaneous removal from natural gas using potassium carbonate aqueous solution in hollow fiber membrane contactor. Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(5), 104130, DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104130
Nuswantara, M, R, P., Priharnanto, W., & Wibawa, G. (2014). Regasification of LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas). Jurnal Teknik ITS, 3(2), 149–152, DOI: 10.12962/j23373539.v3i2.6438
Rao, V. V., Adi Putra, Z., Bilad, M. R., Wirzal, M. D. H., & Nordin, N. A. H. M. (2020). Optimization of lng cold energy utilization via power generation, refrigeration, and air separation. Indonesian Journal of Science and Technology, 5(3), 321–333, DOI: 10.17509/ijost.v5i3.24888
Park, J., You, F., Mun, H., & Lee, I. (2021). Liquefied natural gas supply chain using liquid air as a cold carrier: Novel method for energy recovery. Energy Conversion and Management, 227, 113611, DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113611
Sandler, S.I. (1999). Chemical and Engineering Thermodynamics. Singapore: John Wiley and Sons.
Setiawan, A., Wibowo, A. P., & Rosyid, F. A. (2020). Analisis Pengaruh Ekspor dan konsumsi Batubara terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Indonesia. Teknologi Mineral dan Batubara, 16 (2), 109–124, DOI: 10.30556/jtmb.Vol16.No2.2020.1081
Smith, J.M., Van Ness, H.C & Abbott, M.M. (2005). Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 7th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Sun, H., Zhu, H., Liu, F., & Ding, H. (2014). Simulation and optimization of a novel Rankine power cycle for recovering cold energy from liquefied natural gas using a mixed working fluid. Energy, 1–8, DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.03.128
Wang, M., Zhang, J., & Xu, Q. (2012). Optimal design and operation of a C3MR refrigeration system for natural gas liquefaction. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 39, 84–95, DOI: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2011.12.003
Wang, Z., Han, F., Ji, Y., & Li, W. (2020). Case Studies in Thermal Engineering Analysis on feasibility of a novel cryogenic heat exchange network with liquid nitrogen regeneration process for onboard liquefied natural gas reliquefaction. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 22, 100760, DOI: 10.1016/j.csite.2020.100760
Yoon, S., Oh, J. S., & Kim, J. K. (2020). Dynamic simulation and control of Natural Gas Liquids recovery process. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120349, DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120349
Zhao, Z., Zhao, K., Jia, D., Jiang, P., & Shen, R. (2017). Numerical investigation on the flow and heat transfer characteristics of supercritical liquefied natural gas in an airfoil fin printed circuit heat exchanger. Energies, 10(11), DOI: 10.3390/en10111828
Zohuri, B. (2018). Chapter 2-Properties of Pure Substances. Book Chapter of Physics of Cryogenics (An Ultralow Temperature Phenomenon), 53–79, DOI: 10.1016/b978-0-12-814519-7.00002-1
Article Metrics
Abstract has been read : 988 timesDOWNLOAD PDF file viewed/downloaded: 0 times
DOI: http://doi.org/10.25273/cheesa.v4i1.8316.18-30
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



